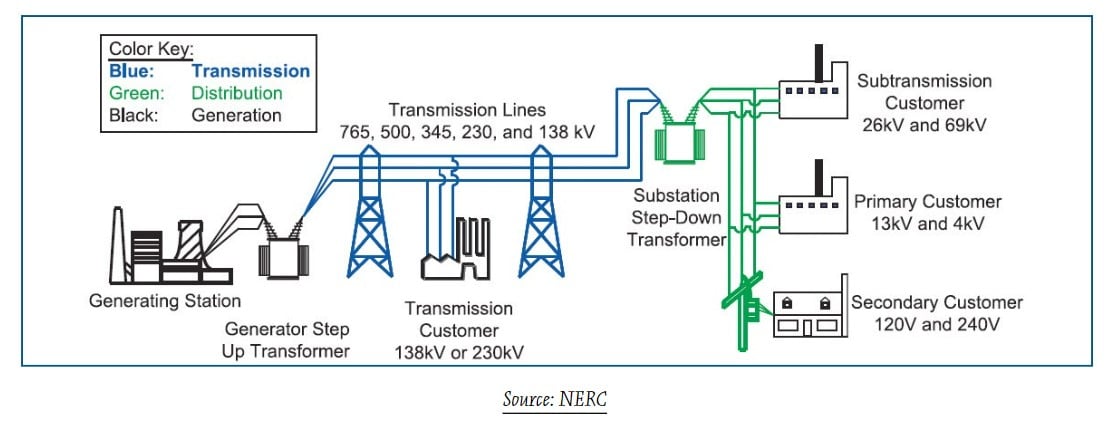
The electric grid is a complex network that delivers electricity from producers to consumers. It includes three main components:
1. Generation: Electricity is produced at power plants using various energy sources like coal, natural gas, nuclear, hydro, wind, and solar.
2. Transmission: High-voltage power lines carry electricity over long distances from power plants to substations. This minimizes energy loss during transport.
3. Distribution: At substations, the high voltage is reduced to lower voltages suitable for homes and businesses. Distribution lines deliver electricity to end-users.
The grid functions by continuously balancing electricity supply and demand to ensure stability. Operators use real-time data to manage the flow of electricity and respond to changes in usage or production. Modern grids incorporate smart technologies to enhance efficiency, reliability, and integration of renewable energy sources.